Source: Drug labeling information submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), updated by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
See also:
Potential for Other Drugs to Affect Lurasidone
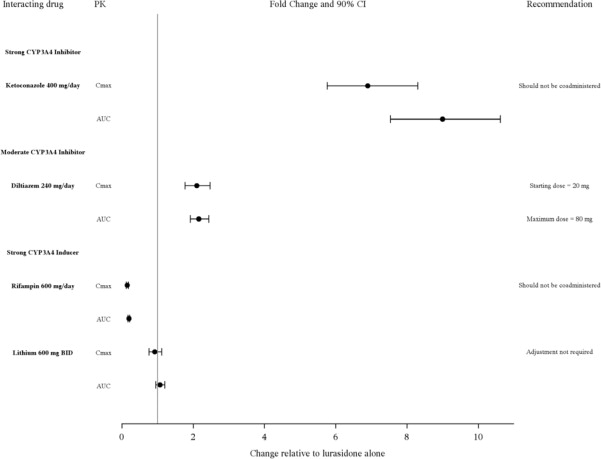
LATUDA is predominantly metabolized by CYP3A4. LATUDA should not be used concomitantly with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, clarithromycin, ritonavir, voriconazole, mibefradil, etc.) or strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, avasimibe, St. John’s wort, phenytoin, carbamazepine, etc.) [see Contraindications (4)]. The LATUDA dose should be reduced to half of the original level when used concomitantly with moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g., diltiazem, atazanavir, erythromycin, fluconazole, verapamil, etc.). If LATUDA is used concomitantly with a moderate CYP3A4 inducer, it may be necessary to increase the LATUDA dose.
Lithium: It is not necessary to adjust the LATUDA dose when used concomitantly with lithium (Figure 1).
Valproate: It is not necessary to adjust the LATUDA dose when used concomitantly with valproate. A dedicated drug-drug interaction study has not been conducted with valproate and LATUDA. Based on pharmacokinetic data from the bipolar depression studies valproate levels were not affected by lurasidone, and lurasidone concentrations were not affected by valproate.
Grapefruit: Grapefruit and grapefruit juice should be avoided in patients taking LATUDA, since these may inhibit CYP3A4 and alter LATUDA concentrations [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Figure 1: Impact of Other Drugs on LATUDA Pharmacokinetics
Potential for Lurasidone to Affect Other Drugs
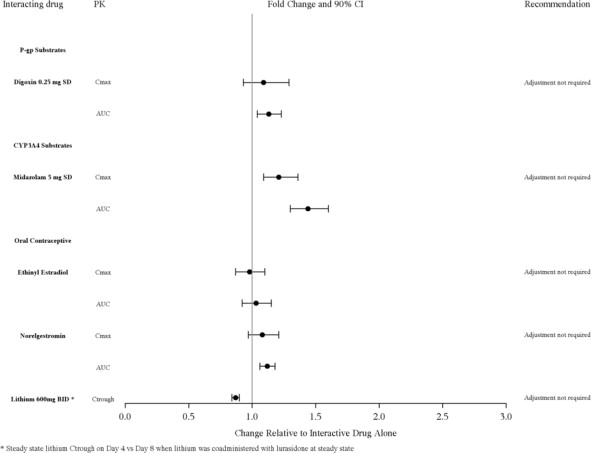
No dose adjustment is needed for lithium, substrates of P-gp, CYP3A4 (Figure 2) or valproate when coadministered with LATUDA. ).
Figure 2: Impact of LATUDA on Other Drugs
Related lurasidone prescribing information



