Methylphenidate is a CNS stimulant approved for the treatment of narcolepsy and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Methylphenidate inhibits the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, increased dopaminergic and noradrenergic activity in the prefrontal cortex may explain its efficacy in ADHD. There are many formulations available, these can be grouped into short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting methylphenidate. When deciding which formulation is the most suitable for a given patient, it is important to consider two parameters: time to initial effect and duration of action.
Mechanism of action
The prefrontal cortex and the role of NE and DA in ADHD
Under normal circumstances, the prefrontal cortex regulates attention, behavior and emotion. Deficits in prefrontal cortex functioning have been linked to ADHD symptoms such as poor impulse control, weak sustained attention and heightened distractibility
. Norepinephrine (NE) and dopamine (DA) are key neurotransmitters for prefrontal functioning, there is an inverted-U dose-response relationship for catecholamines and prefrontal abilities. The images below show the relationship between levels of catecholamine release and prefrontal abilities in fatigued, alert and stressed states.
- Fatigued state: Too little dopamine and norepinephrine, prefrontal abilities are impaired

Fig. 1. Fatigued state
- Alert state: Moderate release of norepinephrine and dopamine, optimal prefrontal functioning

Fig. 2. Alert state
- Stressed state: Excessive catecholamine release, prefrontal abilities impaired

Fig. 3. Stressed state
Methylphenidate inhibits the reuptake of NE and DA
Methylphenidate modulates the activity of DAT and NET
- The dopamine transporter (DAT) influences synaptic concentrations of dopamine.
- The norepinephrine transporter (NET) is in charge of norepinephrine reuptake from the synaptic space to presynaptic neurons.

Fig. 4. Methylphenidate inhibits DAT and NET
Methylphenidate blocks the norepinephrine and dopamine transporters, leading to increased availability of norepinephrine and dopamine at the synaptic space [2] . The difference with amphetamine is that methylphenidate does not promote dopamine release from synaptic vesicles.
Methylphenidate formulations
Short-acting

Short-acting methylphenidate is available as tablet, chewable tablets and a liquid formulation.Dexmethylphenidate is available as tablets. The duration of action of short action formulations is between 3 to 5 hours. Table: Advantages and disadvantages of short-acting formulations
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| May be useful when a top-up of the once-daily dosing is required | Shorter duration than long-acting versions |
| May offer more flexibility | Prone to having peak/trough effects that may be uncomfortable |
- Time to initial effect and duration of action
- Time to initial effect: 20 to 60 minutes
- Duration of action: 3 to 5 hours
Presentations

Fig. 5. Short-acting methylphenidate formulations
- Methylphenidate
- Tablet
- Ritalin
- Methylin
- Chewable tablet
- Methylin CT
- QuilliChew ER
- Liquid
- Methylin Oral Solution
- Tablet
- Dexmethylphenidate
- Tablet
- Focalin
- Tablet
Intermediate-acting

- Time to initial effect and duration of action
- Onset of action: 20–60 minutes
- Duration of action: Up to 8 hours
Wax matrix tablets
- Brand names: Metadate ER, Ritalin SR
- Wax matrix at times can result in an inconsistent release of medication and thus inconsistent effects
Extended-release methylcellulose base
- Brand name: Methylin ER
Long-acting

The following are long-acting methylphenidate formulations: Osmotic Release Oral System (OROS), sustained-release capsules, controlled delivery methylphenidate, Spheroidal Oral Drug Absorption System (SODAS), dexmethylphenidate sustained-release capsules, a transdermal patch and an oral suspension.
Methylphenidate OROS
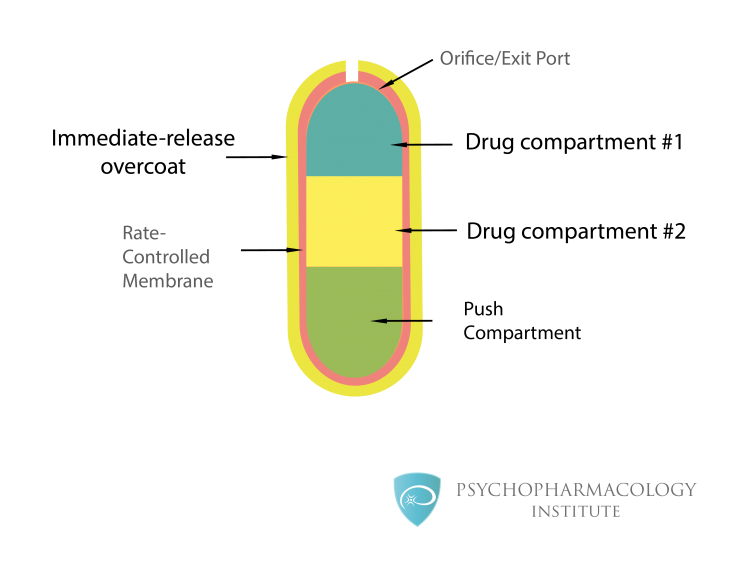
Fig.6. Osmotic release technology
This image shows methylphenidate osmotic release technology. The yellow outer layer contains an immediate release methylphenidate overcoat. The extended release portion has two drug compartments, there is also a push compartment.

Fig.7. Osmotic release technology
Osmotic pressure activates the push compartment so that the system can release methylphenidate from the drug compartments through the orifice [3] .
- Brand name:
- Concerta
- Delivery technology:
- Osmotic Release Oral System (OROS)
- IR/ER ratio (%):
- 22 % IR / 78% ER
- Duration of action:
- Up to 12 hours
Methylphenidate controlled delivery
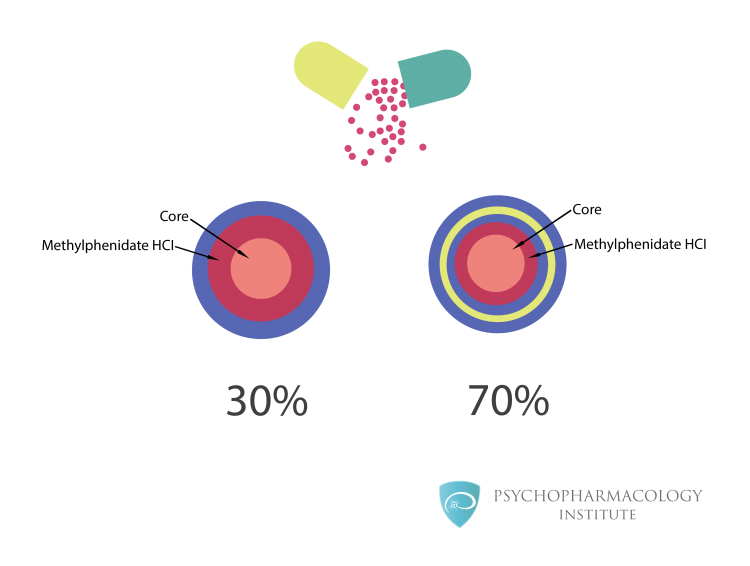
Fig. 8. Diffucaps system
Diffucaps system. Each capsule contains 30% of immediate release beads and 70% of extended release beads.
- Brand names:
- Metadate CD
- Equasym XL
- Delivery technology:
- Diffucaps
- IR/ER ratio (%):
- 30 % IR / 70% ER
- Duration of action:
- Up to 8 hours
- Approximates a twice per day dosing schedule [4]
Methylphenidate SODAS
- Brand name:
- Ritalin LA
- Delivery technology:
- SODAS ( Spheroidal Oral Drug Absorption System)
- Similar to a twice per day dosing schedule
- IR/ER ratio (%):
- 50 % IR / 50 % ER
- Duration of action:
- 8–12 hours
- Two distinct peaks approximately 4 hours apart
Dexmethylphenidate sustained-release capsules
- Brand name:
- Focalin XR
- Mechanical sustained release preparation
- Contains only the d-MPH isomer
- IR/ER ratio (%):
- 50 % IR / 50% ER
- Similar efficacy at a lower dose than methylphenidate
- Duration of action:
- 8–12 hours [5]
Methylphenidate patch
- Brand name
- Daytrana
- Delivery technology:
- Transdermal delivery
- Duration of action:
- 8 – 12 hours
Table: Advantages and disadvantages of the methylphenidate patch
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| May have lower abuse potential than oral formulations | Slower onset than oral formulations |
| May enhance adherence |
Methylphenidate oral suspension
- Brand name:
- Quillivant XR
- Delivery technology:
- Powder that needs to be reconstituted with water
- Duration of action:
- 8 – 12 hours [6]
References
- Arnsten, A. F., & Berridge, C. W. (2014). Catecholamine influences on prefrontal cortex circuits and function. Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Adults and Children, 161. ↩
- Wilens, T. E. (2006). Mechanism of action of agents used in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 67, 32 . ↩
- Katzman, M. A., & Sternat, T. (2014). A Review of OROS Methylphenidate (Concerta®) in the Treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder . CNS drugs, 28(11), 1005–1033. ↩
- Prince, J. B., Wilens, T. E., Spencer, T. J., & Biederman, J. (2015). 10 Stimulants and Other Medications for ADHD. Massachusetts General Hospital Psychopharmacology and Neurotherapeutics, 99. ↩
- Focalin XR (Dexmethylphenidate sustained release) [Prescribing Information] East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals CorporationAccessed May 2015 ↩
- Methylphenidate (Quillivant XR) [Prescribing Information] New York, NY : Pfizer Inc.. Accessed May 2015 ↩



