Olanzapine is a second-generation antipsychotic that acts as an antagonist at 5HT2A and D2 receptors.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of olanzapine, as with other drugs having efficacy in schizophrenia, is unknown. However, it has been proposed that this drug’s efficacy in schizophrenia is mediated through a combination of dopamine and serotonin type 2 (5HT2) antagonism. The mechanism of action of olanzapine in the treatment of acute manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder is unknown.
The video below discusses the relationship between 5HT2A/D2 antagonism in the mechanism of action of second-generation antipsychotics:
Pharmacodynamics
The image below shows a schematic view of the pharmacodynamic profile of the drug.
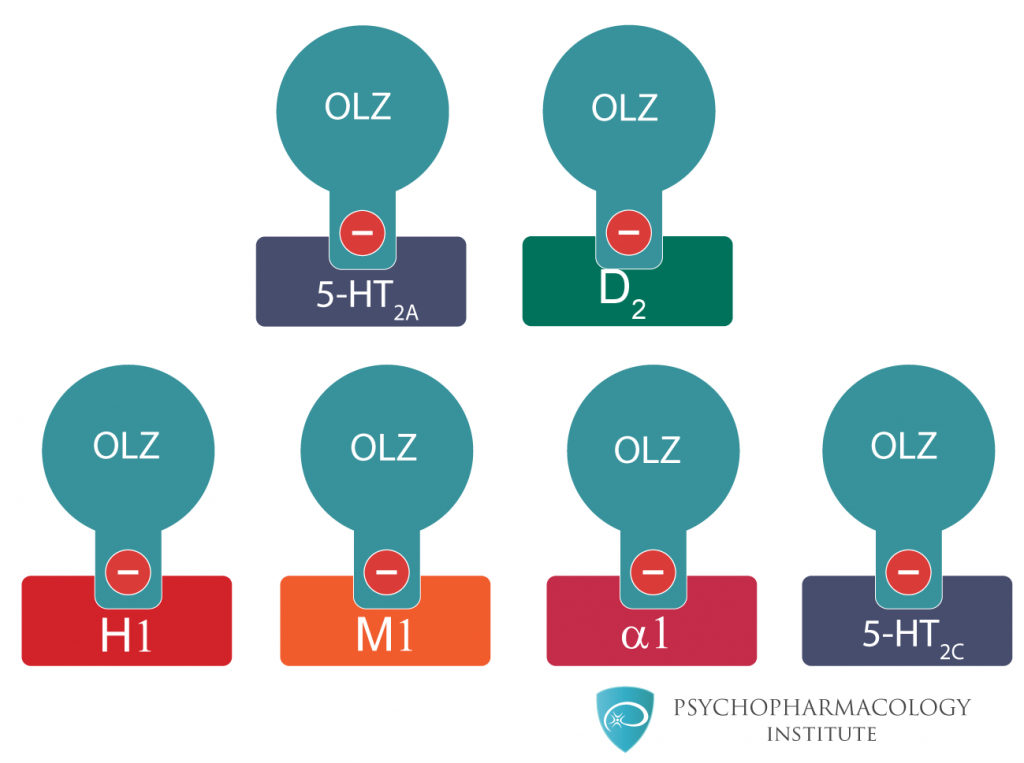
Olanzapine pharmacodynamics: a schematic representation of its most relevant affinities .
Olanzapine binds with high affinity to the following receptors: serotonin 5HT2A/2C, 5HT6 (Ki=4, 11, and 5 nM, respectively), dopamine D1-4 (Ki=11-31 nM), histamine H1 (Ki=7 nM), and adrenergic α1 receptors (Ki=19 nM). Olanzapine is an antagonist with moderate affinity binding for serotonin 5HT3 (Ki=57 nM) and muscarinic M1-5 (Ki=73, 96, 132, 32, and 48 nM, respectively). Olanzapine binds weakly to GABAA, BZD, and β-adrenergic receptors (Ki>10 μM). Antagonism at receptors other than dopamine and 5HT2 may explain some of the other therapeutic and side effects of olanzapine.
Olanzapine’s antagonism of muscarinic M1-5 receptors may explain its anticholinergic-like effects. Olanzapine’s antagonism of histamine H1 receptors may explain the somnolence observed with this drug. Olanzapine’s antagonism of adrenergic α1 receptors may explain the orthostatic hypotension observed with this drug.
Related Olanzapine Information
- Olanzapine Indications: FDA-Approved Uses
- Olanzapine Interactions
- Olanzapine Pharmacokinetics
- Olanzapine Adverse Effects
References and Further Reading
- Drug labeling information submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), updated by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- McCormick PN, Kapur S, Graff-Guerrero A, Raymond R, Nobrega JN, Wilson AA. The antipsychotics olanzapine, risperidone, clozapine, and haloperidol are D2-selective ex vivo but not in vitro . Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35(8):1826-3



