This tutorial discusses:
- Brain abnormalities found in patients suffering from bipolar disorder
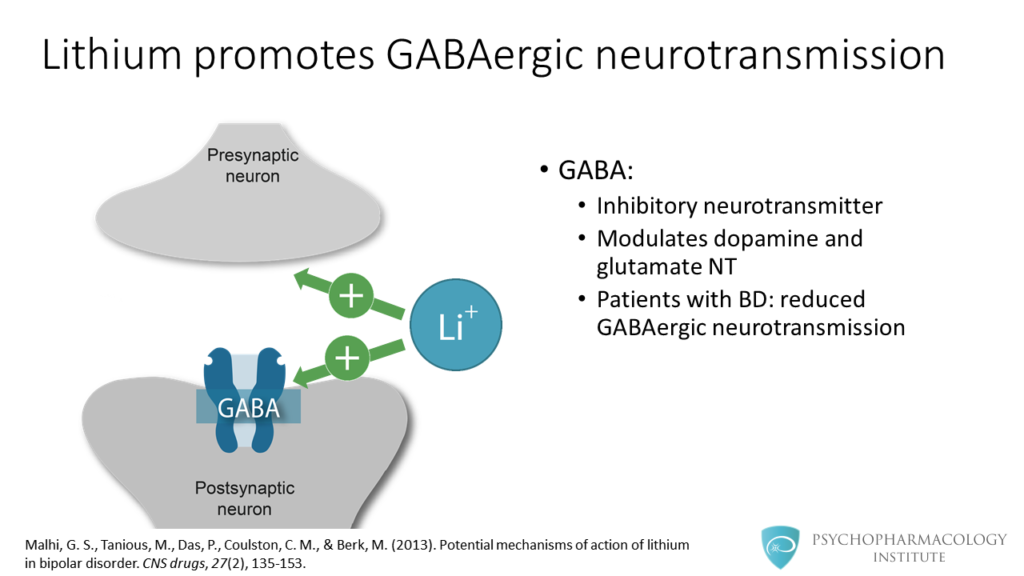
- How lithium modulates dopamine, glutamate and GABA
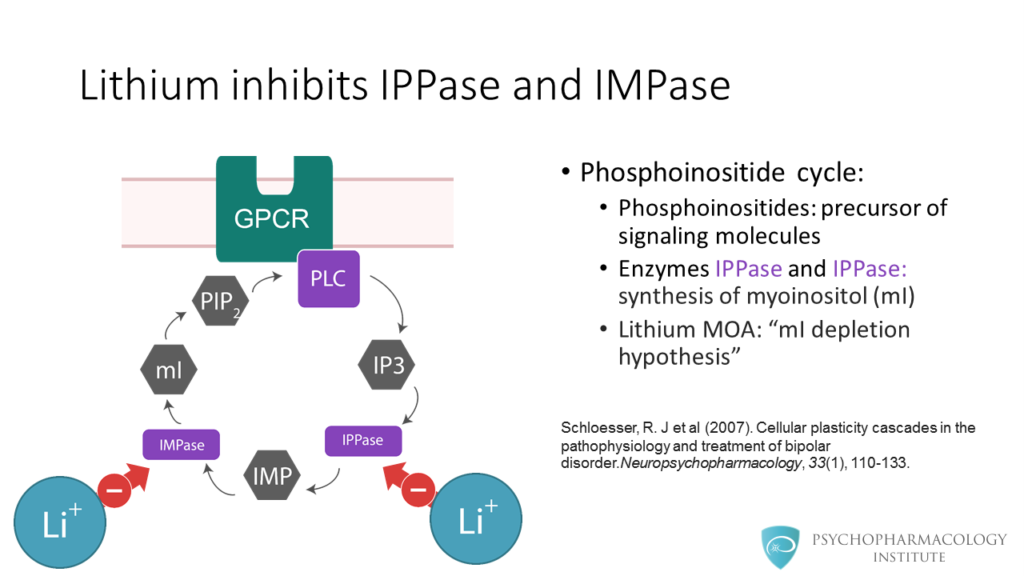
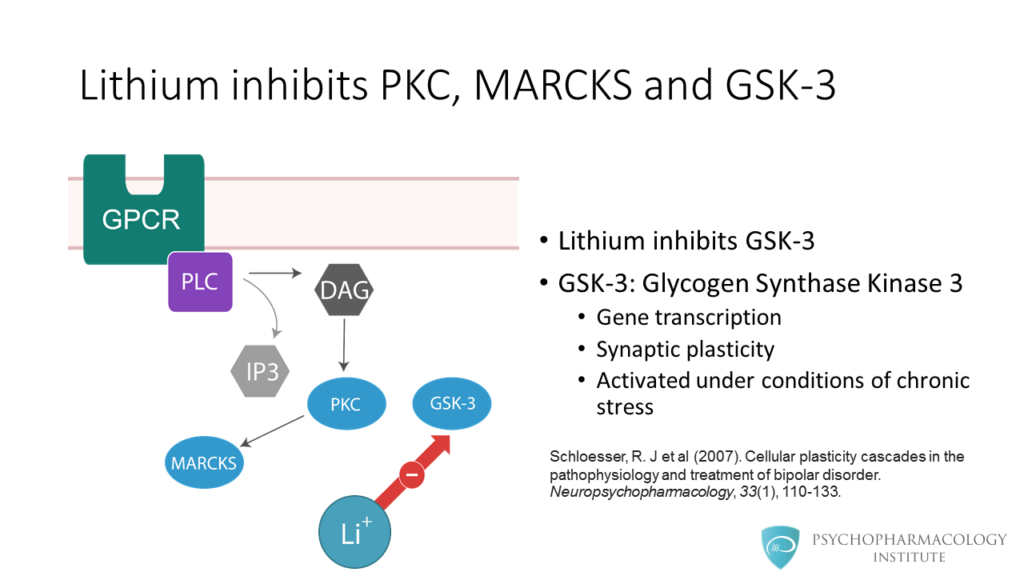
- Intracellular changes associated with lithium use (effects on proteins such as PKC, MARCKS, GSK-3, IPPase and IMPase)
Lithium MOA: Text Version











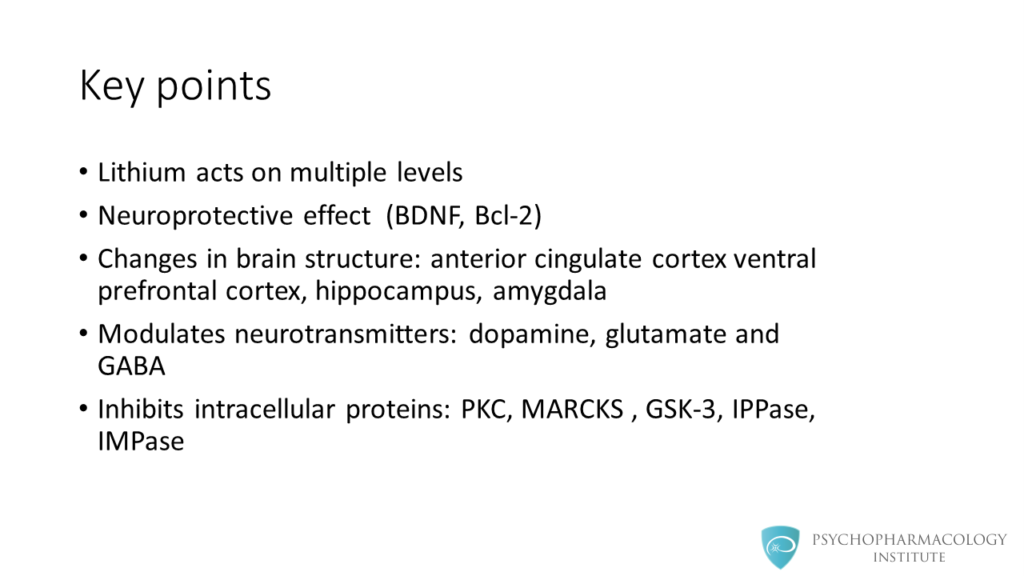
Key Points
The key points are the following:
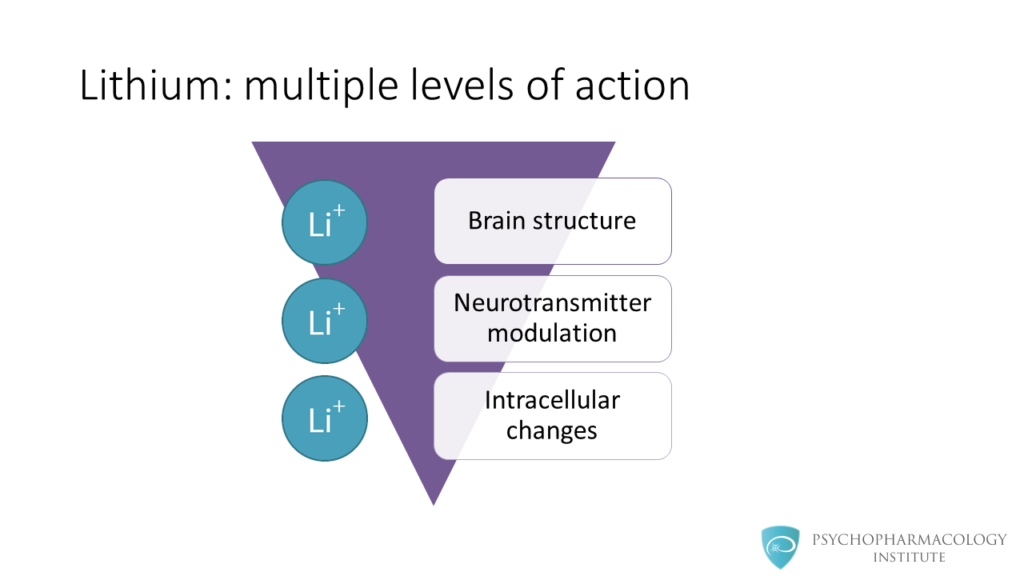
- Lithium acts on multiple levels, from the macroscopic anatomy to microscopic intracellular signaling.
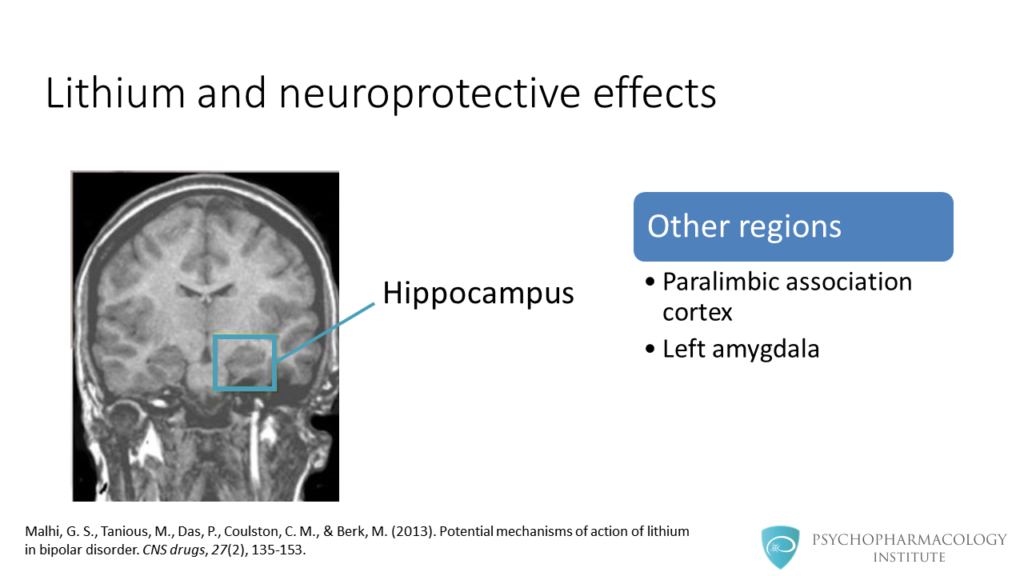
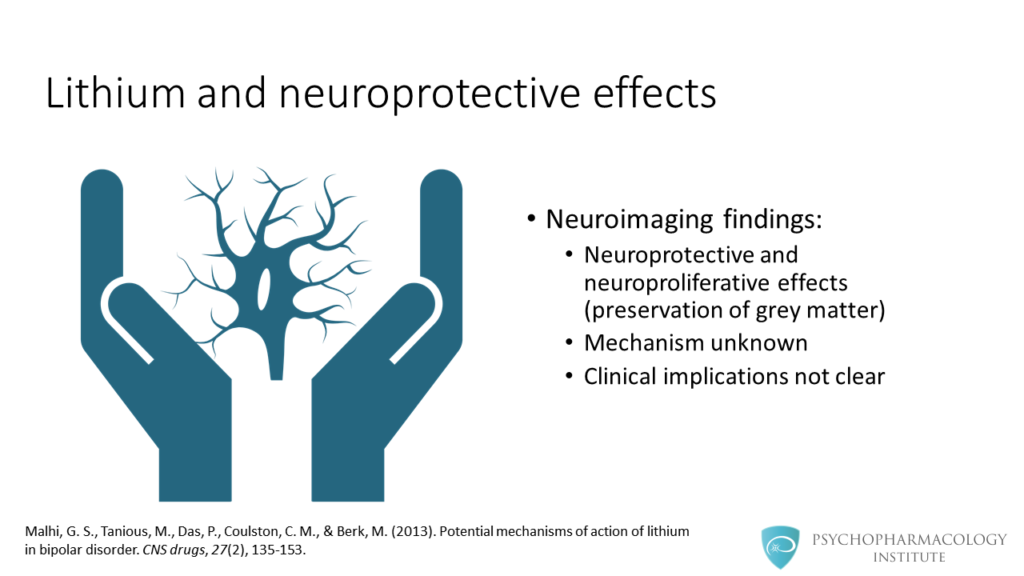
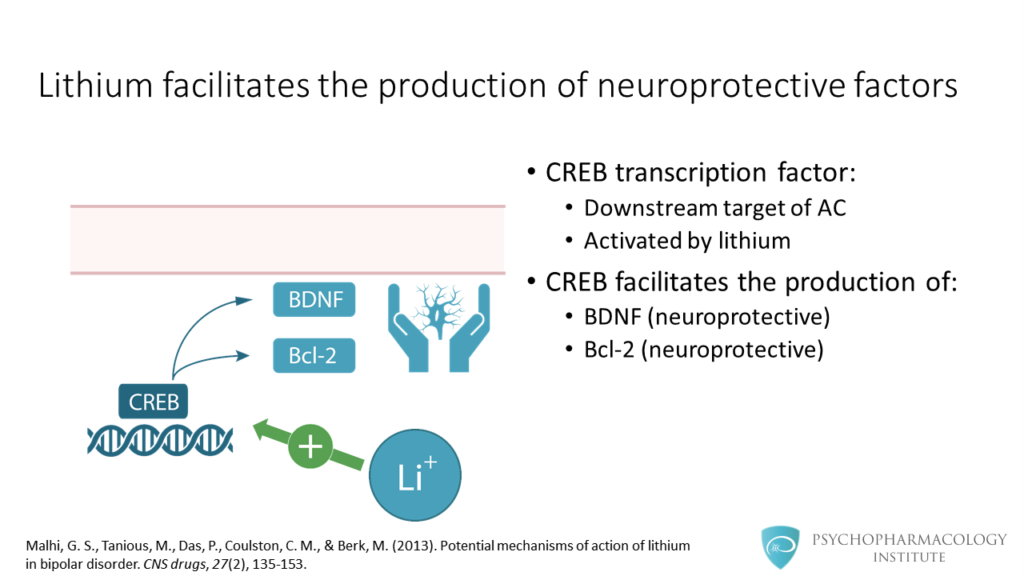
- Lithium use is associated with a neuroprotective effect, factors such as BDNF and BCL2 have been implicated in this effect.
- There are changes in brain structure associated with lithium use, some of these structures are the anterior cingulate cortex, the ventral prefrontal cortex, the hippocampus and the amygdala.
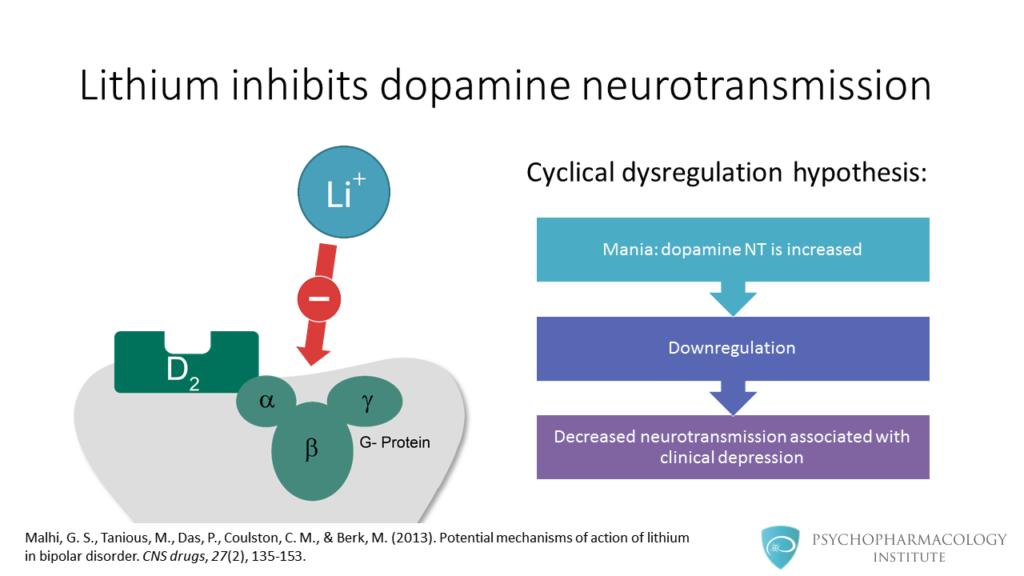
- At the neurotransmitter level, lihium modulates dopamine, glutamate and GABA neurotransmission.
- At the intracellular signaling level lithium inhibits proteins such as PKC, MARCKS, GSK-3, IPPase and IMPase
References
- Malhi, G. S., Tanious, M., Das, P., Coulston, C. M., & Berk, M. (2013). Potential mechanisms of action of lithium in bipolar disorder . CNS drugs, 27(2), 135-153.
- Schloesser, R. J et al (2007). Cellular plasticity cascades in the pathophysiology and treatment of bipolar disorder .Neuropsychopharmacology, 33(1), 110-133.



