Besides being a SERT inhibitor, fluvoxamine is an agonist at sigma 1 receptors. The drug is approved in the US for the treatment of OCD but not depression. This is interesting as this is a widely used antidepressant in other countries. Fluvoxamine has the potential for drug-drug interactions through inhibition of CYP 450 isoenzymes. The dosage range goes from 100 to 300 mg/day.

Let’s summarize some of the most clinically relevant features of fluvoxamine. Besides being a SERT inhibitor, fluvoxamine is an agonist at sigma 1 receptors. The drug is approved in the US for the treatment of OCD but not depression. This is interesting as this is a widely used antidepressant in other countries. Fluvoxamine has the potential for drug-drug interactions through inhibition of CYP 450 isoenzymes. We’ll see in a minute more details about this. The dosage range goes from 100 to 300 mg/day.
Pharmacology and MOA
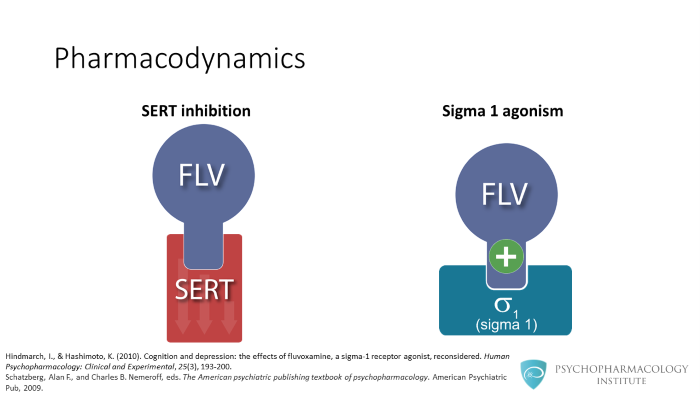
Like other SSRIs, fluvoxamine selectively inhibits the SERT transporter, it is a more potent inhibitor of serotonin reuptake than the tricyclic antidepressants. Fluvoxamine has minimal affinity for muscarinic, 5HT2C and alfa 1 receptors. A feature worth noting is its affinity for sigma 1 receptors. The role of sigma receptors is not very clear, studies in animal models suggest their activation might be involved in cognitive improvement in depression. This is an area of active research.
Clinical Uses
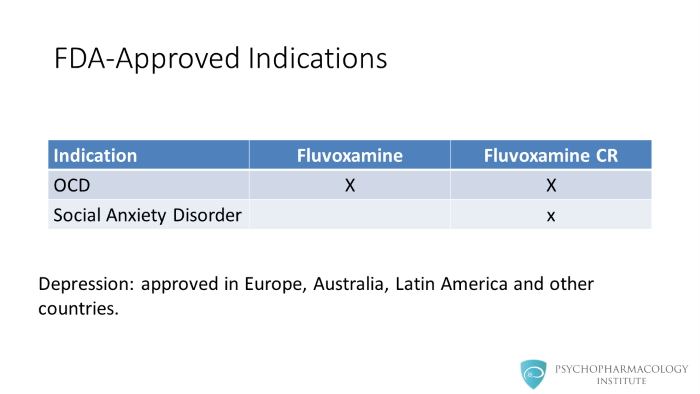
Fluvoxamine is approved as immediate release and controlled release formulations The immediate release formulation is approved for OCD and the controlled release for OCD and social anxiety disorder. In the US, fluvoxamine is not approved for the treatment of depression. However, it is approved for this use in Europe, Australia, Latin America and other countries.

Other clinical uses include anxiety disorders such as panic disorder,
and posttraumatic stress disorder.
Pharmacokinetics

The pharmacokinetics of fluvoxamine is interesting in terms of half life and CYP 450 interactions. Fluvoxamine has a half life of 9 to 28 hours, this requires twice a day dosing for the immediate release formulation, the controlled release formulation can be administered once daily. Fluvoxamine inhibits a number of CYP 450 isoenzymes, as we will see in the next slides.

Fluvoxamine inhibits four CYP 450 isoenzymes, we are going to focus on two of them: CYP 1A2 and CYP 3A4. . In vitro data shows that fluvoxamine inhibits two other isoenzymes, these are CYP 2C9 and C219.
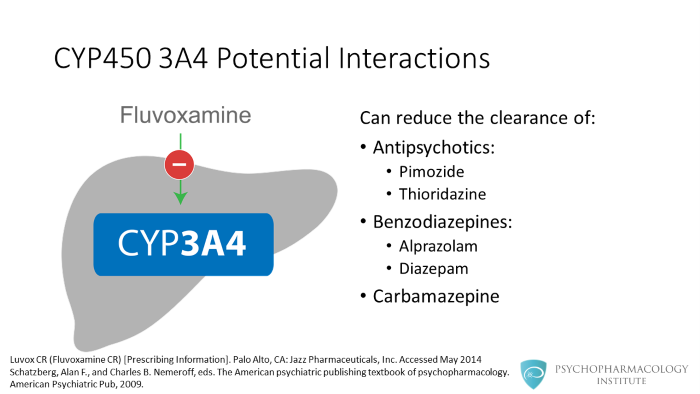
What happens when fluvoxamine inhibits CYP 3A4? This isoenzyme is involved in the clearance of some antipsychotics, benzodiazepines and carbamazepine. So, fluvoxamine can reduce the clearance of the antipsychotics pimozide and thioridazine, the benzodiazepines alprazolam and diazepam and the anticonvulsant carbamazepine.
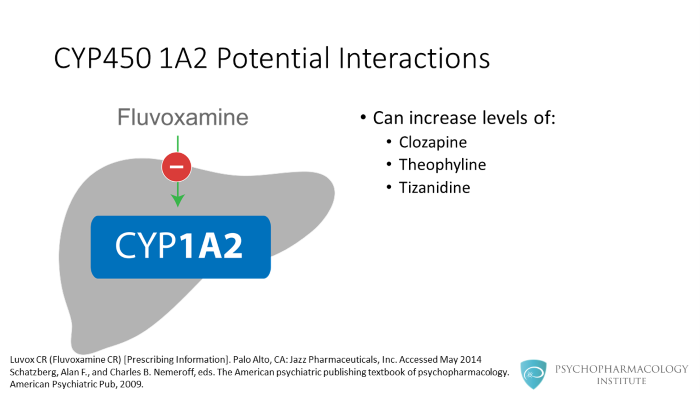
The other important enzyme inhibited by fluvoxamine is CYP 1A2. Fluvoxamine can increase the levels of clozapine, theophylline and tizanidine.
Adverse Effects

Regarding adverse effects fluvoxamine has a profile similar to other SSRIs. Postmarketing clinical studies show that the most common side effects are: nausea, somnolence and asthenia. In a metaanalysis by Serretti and colleagues fluvoxamine was found to have “no transient or negligible effect” on weight gain. Fluvoxamine is classified as pregnancy category C.
Prescribing information
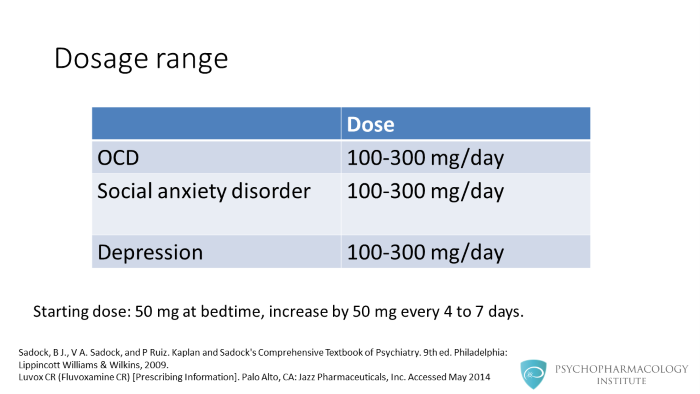
Fluvoxamine is FDA-approved for OCD and social anxiety disorder. For these two indications the therapeutic range is between 100 to 300 mg/day. Fluvoxamine is commonly used in other countries for depression in the same range, but response is commonly seen in the 100 to 200 mg/day range. The starting dose is 50 mg administered at bedtime. This dose may be increased by 50 mg every 4 to 7 days.
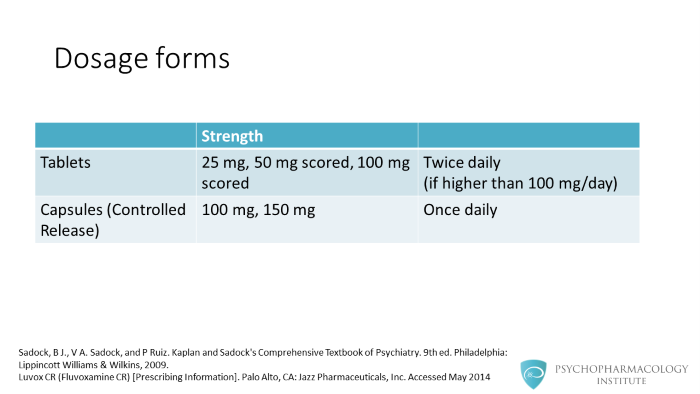
Fluvoxamine is available as immediate release tablets and controlled release capsules. Tablets of 25 mg, 50 mg scored and 100 mg scored. According to the manufacturer, if fluvoxamine is dosed higher than 100 mg, it needs to be given twice daily. This is an important difference with controlled release capsules of 100 and 150 mg, as they have the advantage of once daily dosing.
Other SSRI videos
- Fluvoxamine Essentials: Mechanism of Action, Indications, Pharmacokinetics and Dosing
- Sertraline Essentials: Mechanism of Action, Indications, Pharmacokinetics and Dosing
- Citalopram and Escitalopram: A Summary of Key Differences and Similarities
- The Psychopharmacology of Paroxetine: An Illustrated Summary for Prescribers
This video is also available in Spanish: “
Fluvoxamina: farmacodinamia, indicaciones, efectos adversos, farmacocinética y posología
“
References
- Hindmarch, I., & Hashimoto, K. (2010). Cognition and depression: the effects of fluvoxamine, a sigma‐1 receptor agonist, reconsidered . Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental, 25(3), 193-200.
- Schatzberg, Alan F., and Charles B. Nemeroff, eds. The American psychiatric publishing textbook of psychopharmacology . American Psychiatric Pub, 2009.
- Luvox CR (Fluvoxamine CR) [Prescribing Information]. Palo Alto, CA: Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Accessed May 2014.
- Serretti, A., & Mandelli, L. (2010). Antidepressants and body weight: a comprehensive review and meta-analysis . The Journal of clinical psychiatry,71(10), 1259-1272.
- Sadock, B J., V A. Sadock, and P Ruiz. Kaplan and Sadock’s Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009.



