Slides and Transcript
Slide 1 of 13
In this fifth video about benzodiazepine prescribing, I will discuss the major risks of benzodiazepine use.
Slide 2 of 13
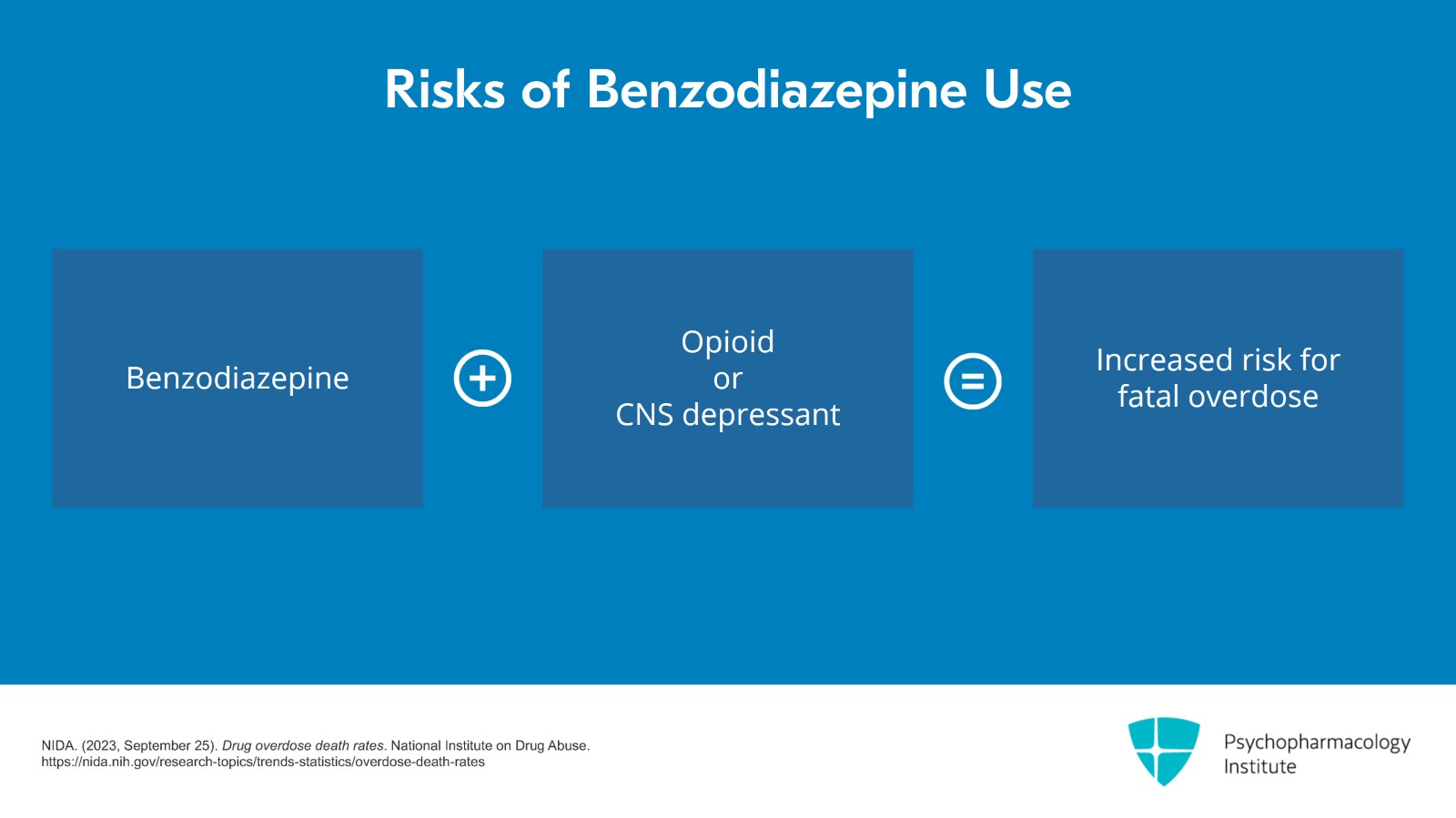
One of the risks with benzodiazepines that's gotten the most publicity is the fact that when a benzodiazepine is used in conjunction with an opioid or other central nervous system depressant, the risk for fatal overdose increases greatly.
References:
- NIDA. (2023, September 25). Drug overdose death rates. National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/trends-statistics/overdose-death-rates
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.
Slide 3 of 13
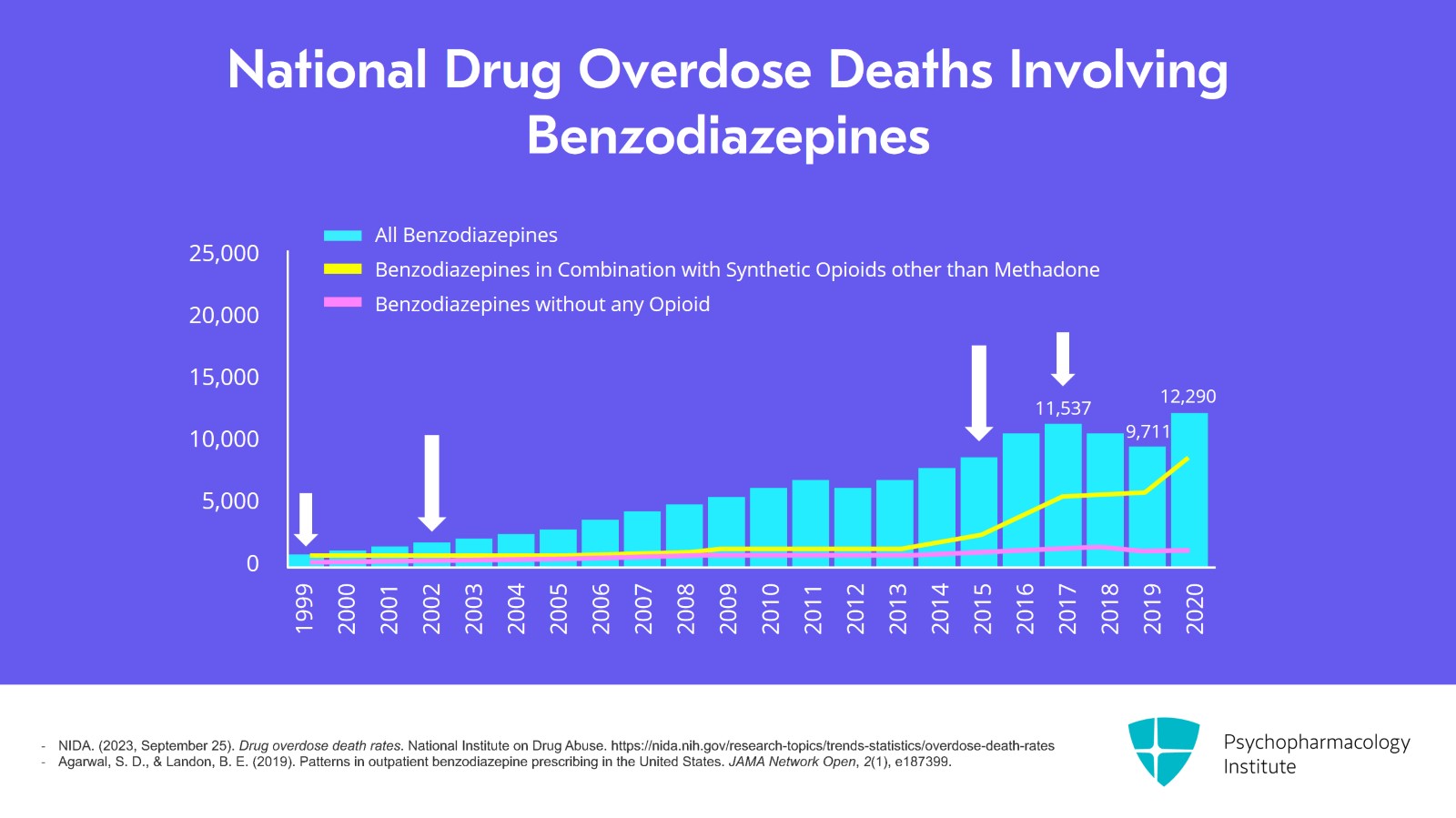
This can be seen in this graph of national drug overdose deaths that involved a benzodiazepine in all ages between 1999 and 2020. Between 2002 and 2015, there is a 4.3-fold increase in the number of deaths involving benzodiazepines. Just to drive home the sheer magnitude of this, you can see that overdose deaths involving benzodiazepines increased from 1,135 in 1999 and 18 years later, this was 11,537. There's then been some fluctuations over time but overall a drastic increase.
References:
- NIDA. (2023, September 25). Drug overdose death rates. National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/trends-statistics/overdose-death-rates
- Agarwal, S. D., & Landon, B. E. (2019). Patterns in outpatient benzodiazepine prescribing in the United States. JAMA Network Open, 2(1), e187399.
Slide 4 of 13
Alone, benzodiazepines do not have a high risk of fatal overdose. However, when they become combined with central nervous system depressants, especially opioids, the risk is lethal. Opioids play a role in about 75% of the deaths involving benzodiazepines.
References:
- NIDA. (2023, September 25). Drug overdose death rates. National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/trends-statistics/overdose-death-rates
- Agarwal, S. D., & Landon, B. E. (2019). Patterns in outpatient benzodiazepine prescribing in the United States. JAMA Network Open, 2(1), e187399.
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.
Slide 5 of 13
However, despite this known lethal combination, estimates are that 35% of patients receive a benzodiazepine script while also having a co-prescription for an opioid. This corresponds to patients receiving both prescriptions at about 10% of all outpatient visits each year.
References:
- NIDA. (2023, September 25). Drug overdose death rates. National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/trends-statistics/overdose-death-rates
- Agarwal, S. D., & Landon, B. E. (2019). Patterns in outpatient benzodiazepine prescribing in the United States. JAMA Network Open, 2(1), e187399.
Slide 6 of 13
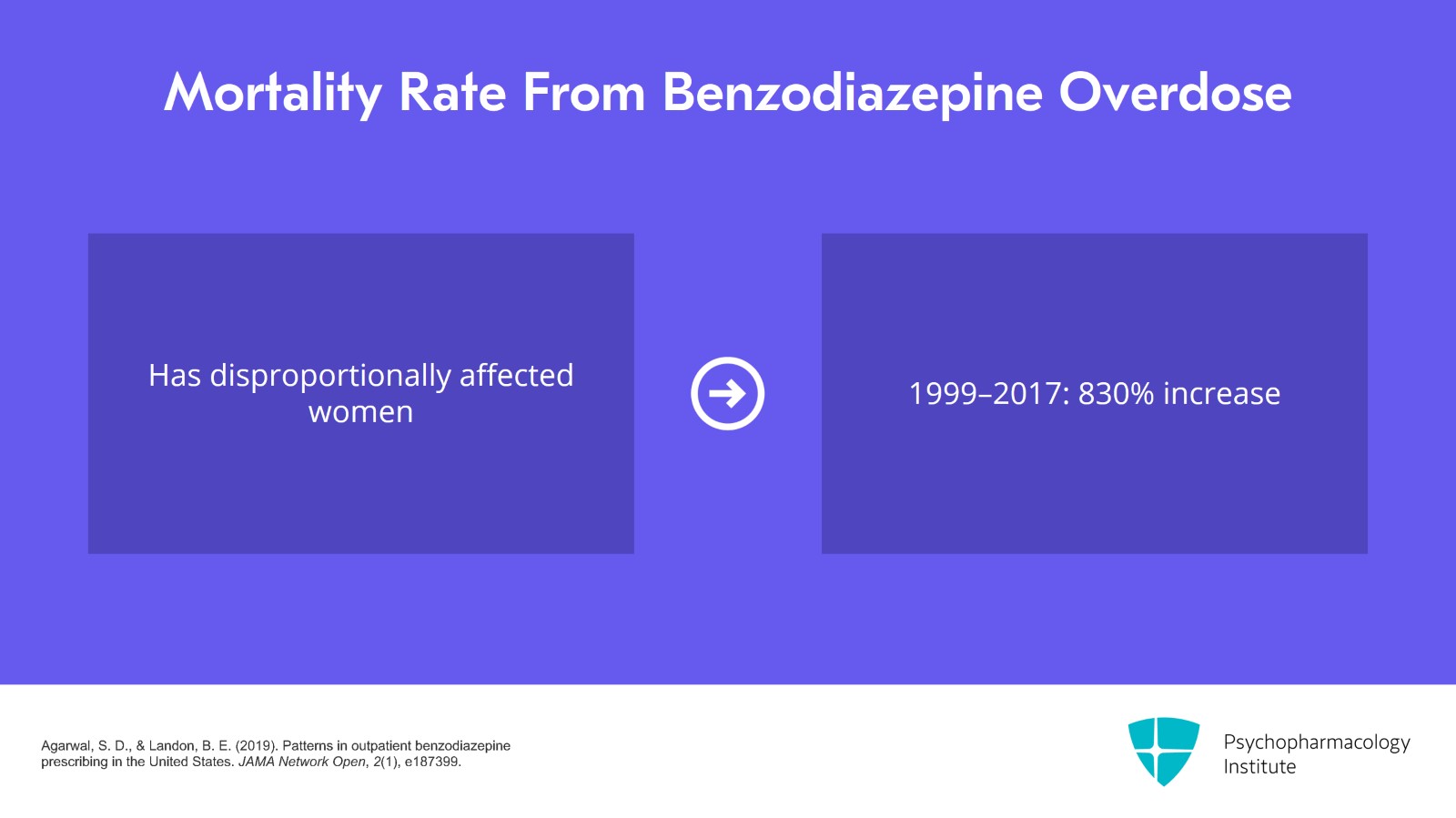
Even more shocking is how the increased mortality rate from overdose involving a benzodiazepine has disproportionally affected women between the ages of 30 and 64. So between 1999 and 2017, there was an 830% increase – and yes, that is 830, not 83 or 8.3 and I double-checked the reference because it sounds so huge – but an 830% increase in women overdosing and involving a benzodiazepine. This is thought to be in part because women are more likely to be prescribed benzodiazepines. They present more often to be treated for anxiety and depression and benzodiazepines are one of the medications that is frequently prescribed to them for these reasons.
References:
- Agarwal, S. D., & Landon, B. E. (2019). Patterns in outpatient benzodiazepine prescribing in the United States. JAMA Network Open, 2(1), e187399.
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.
Slide 7 of 13
Some important things to keep in mind that I like to share with patients about this risk of combining benzodiazepines and opioids whether prescribed or, or illicitly used is that the risk of opioid overdose increases fivefold during the first 90 days of a concurrent prescription with a benzodiazepine. This can be thought of as occurring due to the lack of tolerance to the combined sedation from the two and combined respiratory depression.
References:
- Agarwal, S. D., & Landon, B. E. (2019). Patterns in outpatient benzodiazepine prescribing in the United States. JAMA Network Open, 2(1), e187399.
Slide 8 of 13
In 2016, the FDA issued a black box warning about the serious risk of combining benzodiazepines and opioids especially the increased risk of overdose. Unfortunately, this warning also led to individuals being denied access to medication for addiction treatment for opioid use disorder if they were using a benzodiazepine or prescribed a benzodiazepine.
References:
- FDA. (2016). FDA drug safety communication. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communication-fda-warns-about-serious-risks-and-death-when-combining-opioid-pain-or
- Hernandez, I., He, M., Brooks, M. M., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Exposure-response association between concurrent opioid and benzodiazepine use and risk of opioid-related overdose in Medicare part D beneficiaries. JAMA Network Open, 1(2), e180919.
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.
Slide 9 of 13
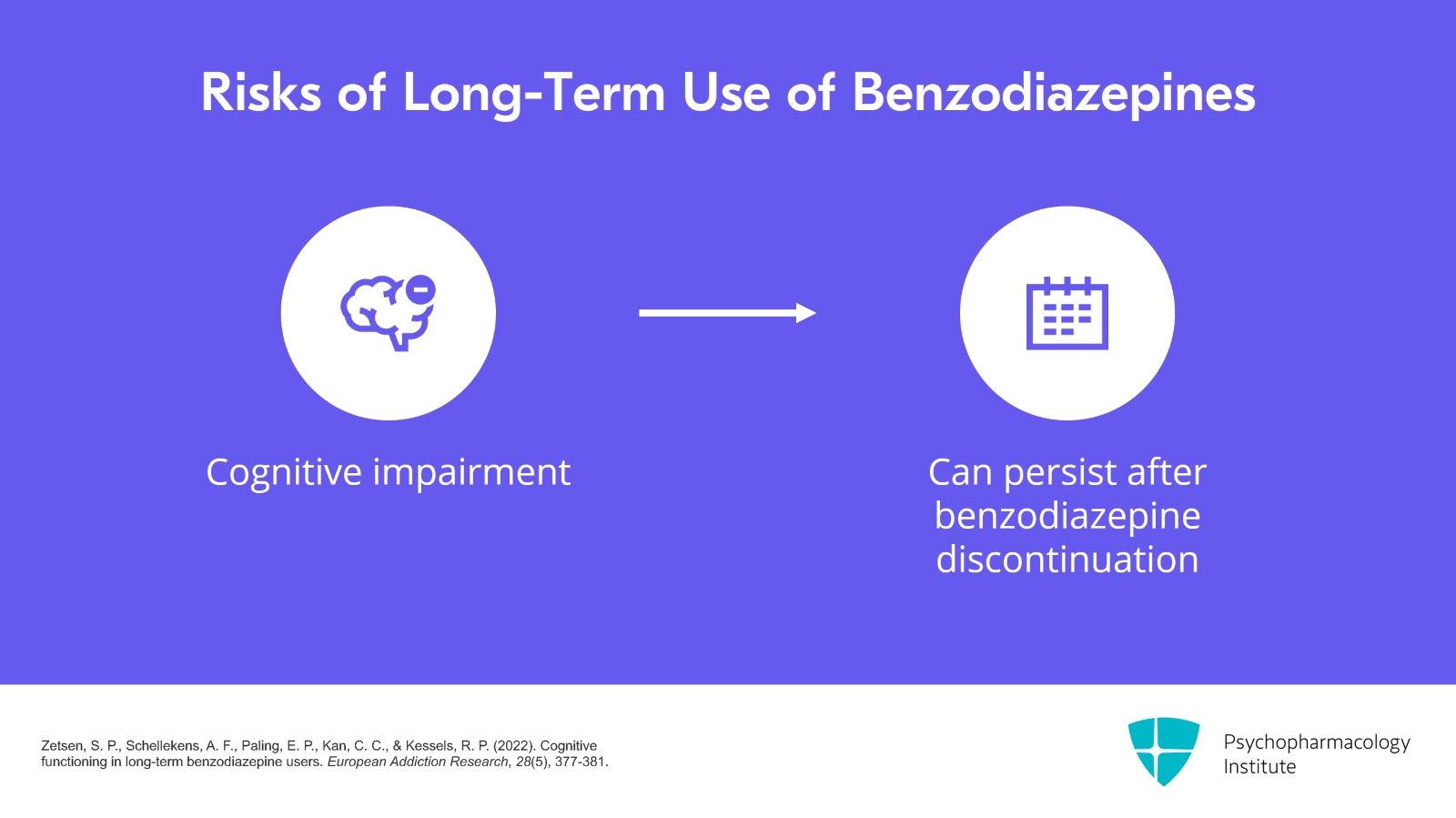
I've already talked some about cognitive impairment being an adverse effect and I really do think of it as one of the major risks associated with long-term benzodiazepine use. Again, a meta-analysis looking at long-term use of diazepam showed that it led to cognitive impairment that lasted well after discontinuation.
References:
- Zetsen, S. P., Schellekens, A. F., Paling, E. P., Kan, C. C., & Kessels, R. P. (2022). Cognitive functioning in long-term benzodiazepine users. European Addiction Research, 28(5), 377-381.
Slide 10 of 13
Another major risk of benzodiazepine use is the risk of motor vehicle accidents. One observational study found that driving while on a benzodiazepine was equivalent to driving with a blood alcohol level of 0.05 to 0.079. And there's a significant increased risk of falls and hip fractures. One study found risk of hip fractures increased 50% for individuals on a benzodiazepine.
References:
- Finkle, W. D., Der, J. S., Greenland, S., Adams, J. L., Ridgeway, G., Blaschke, T., Wang, Z., Dell, R. M., & VanRiper, K. B. (2011). Risk of fractures requiring hospitalization after an initial prescription for zolpidem, alprazolam, lorazepam, or diazepam in older adults. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 59(10), 1883-1890.
- Stone, B. T., Correa, K. A., Brown, T. L., Spurgin, A. L., Stikic, M., Johnson, R. R., & Berka, C. (2015). Behavioral and neurophysiological signatures of benzodiazepine-related driving impairments. Frontiers in Psychology, 6.
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.
Slide 11 of 13
So to summarize the key points for this video, concurrent use of benzodiazepines and opioids, whether prescribed or illicit, greatly increases the risk of overdose. Seventy-five percent of benzodiazepine overdoses involved opioids.
Slide 12 of 13
The other major risks associated with long-term benzodiazepine use are cognitive impairment, motor vehicle accidents, and increased risk of hip fractures.
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.