Learning Objectives:
After completing this activity, the learner will be able to:
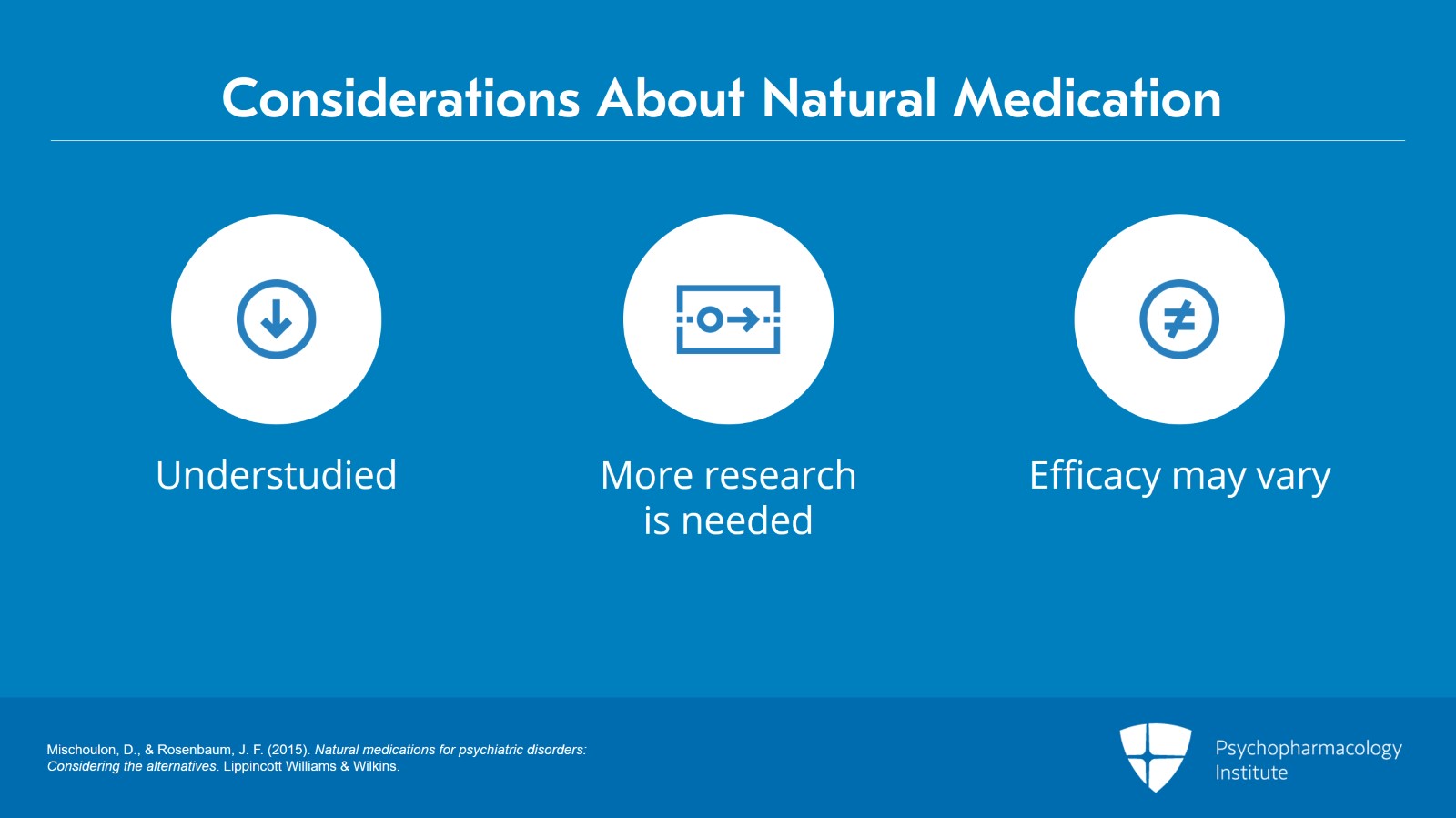
- Evaluate the evidence-based applications and benefits of natural medication in psychiatric treatments.
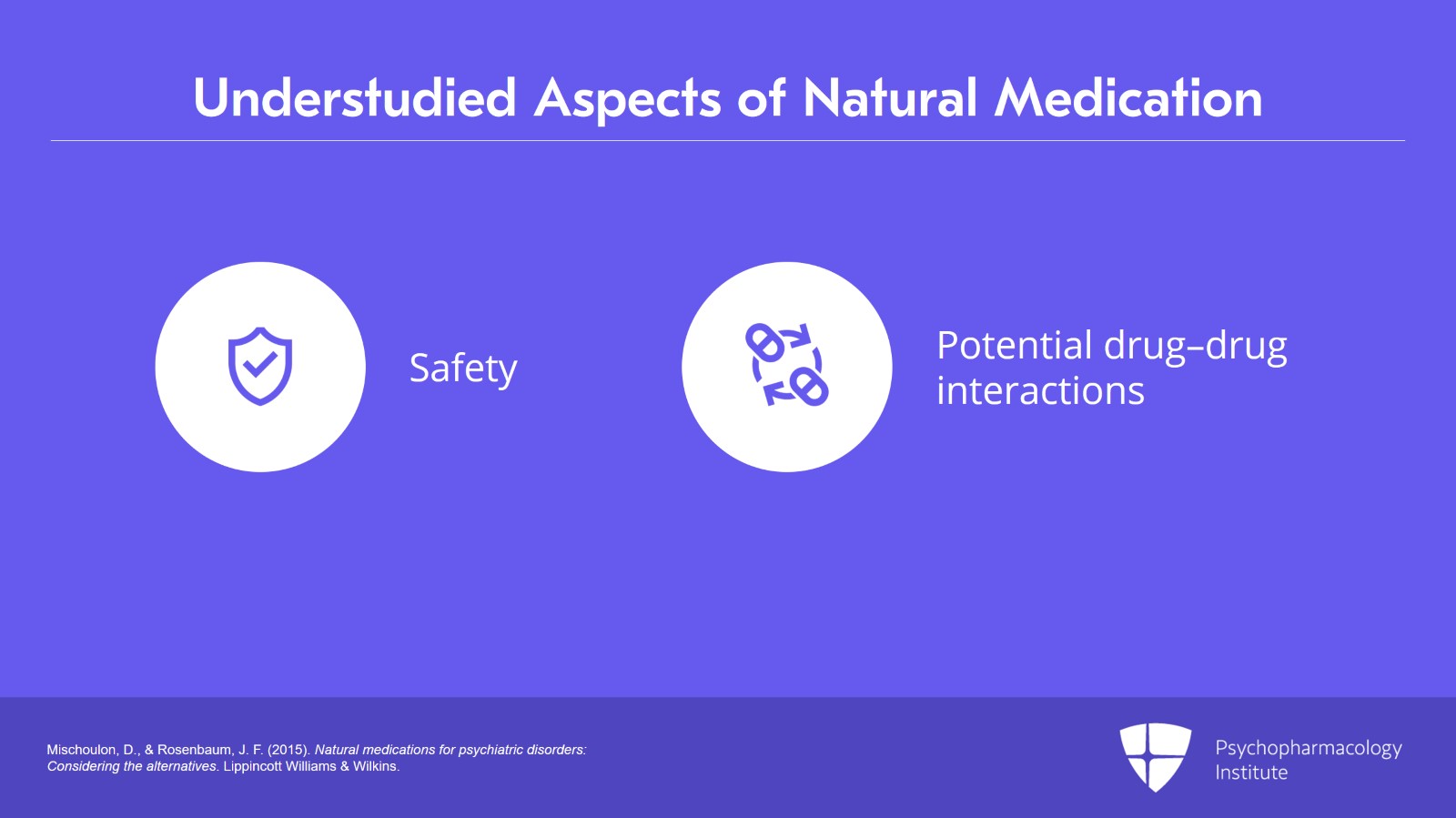
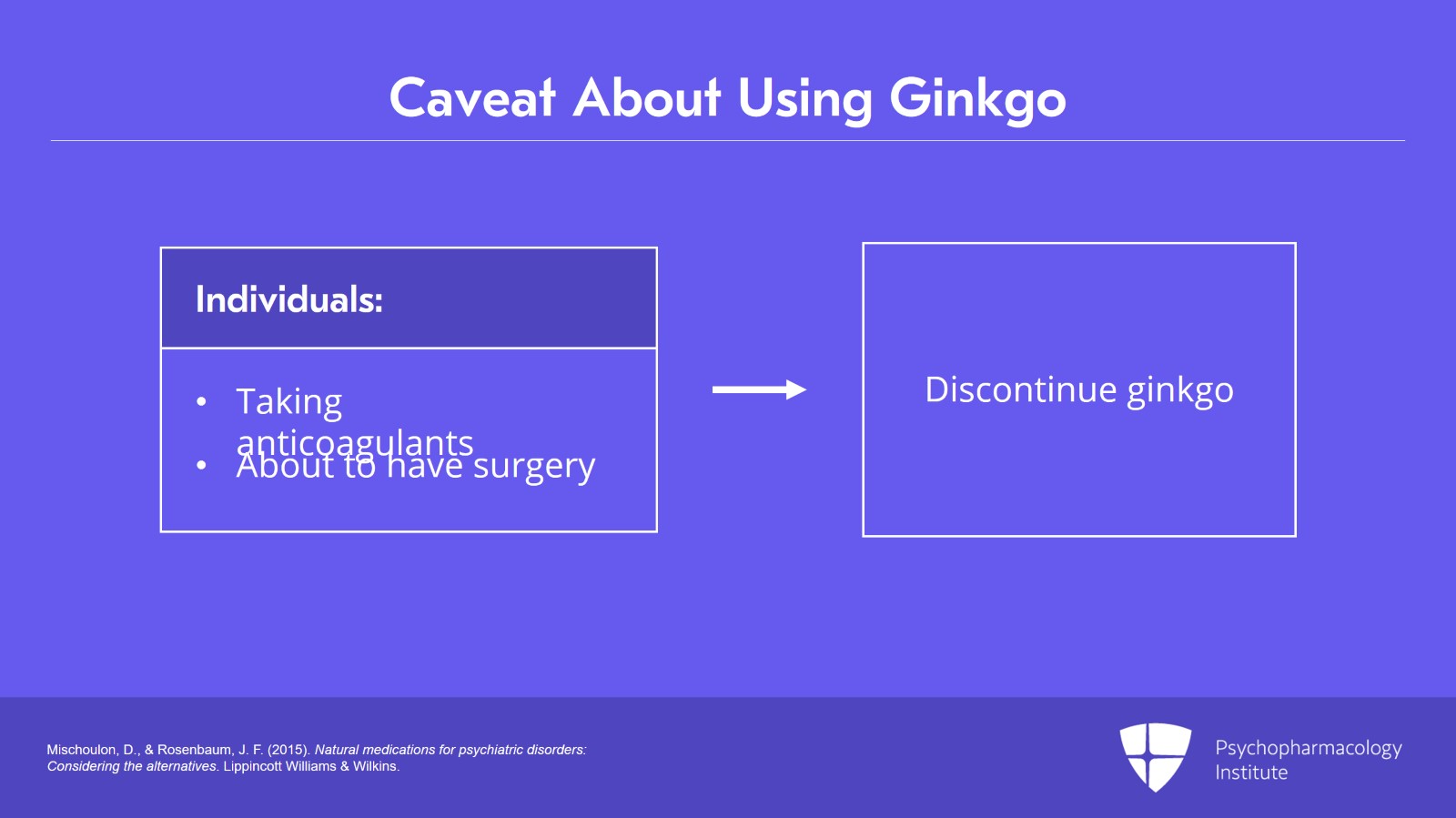
- Analyze the potential risks and side effects of using natural medication in psychiatric treatments.
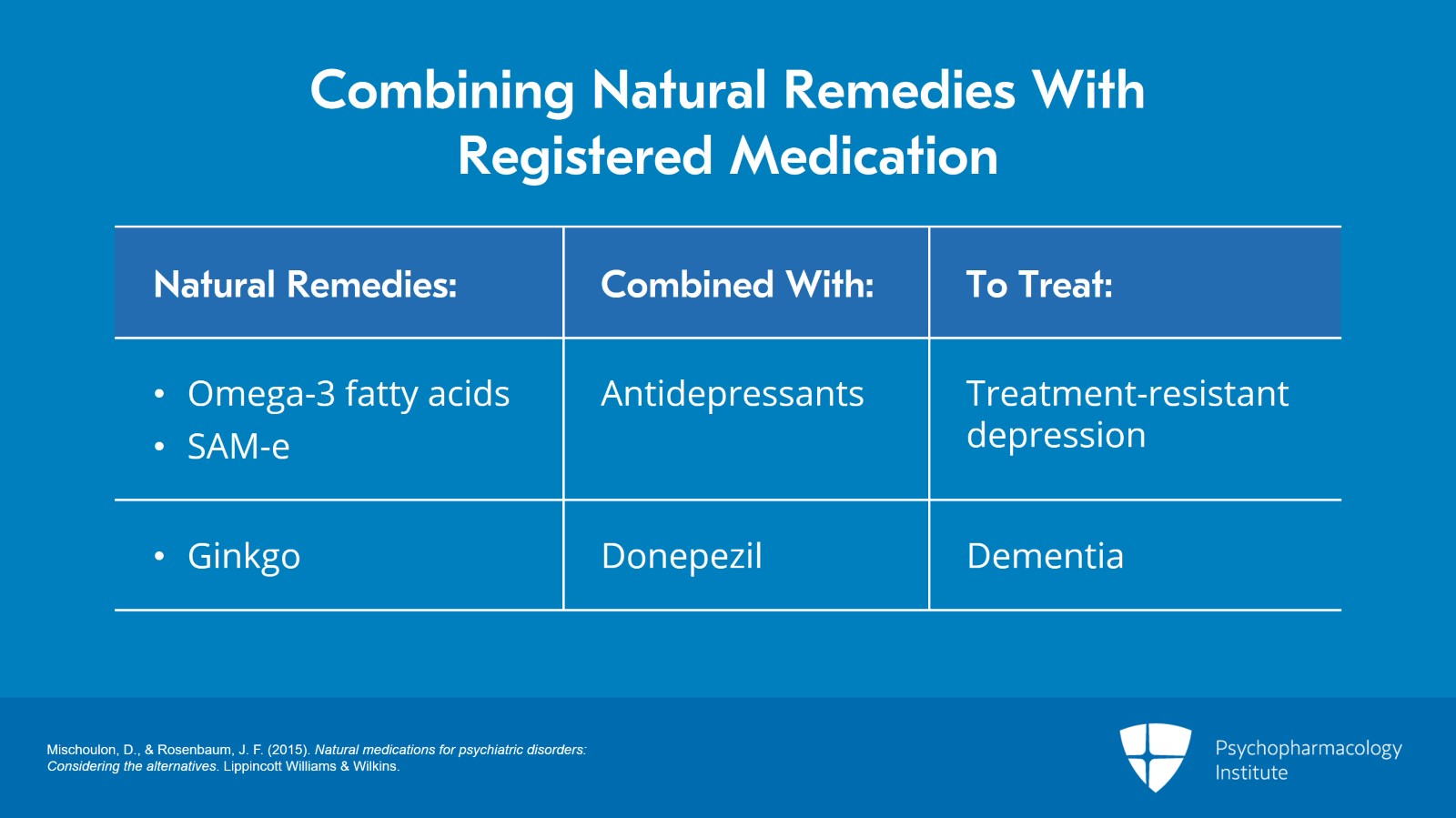
- Identify potential combinations of natural remedies and acquire strategies to optimize their use in psychiatric care.
Original Release Date: November 1, 2023
Review and Re-release Date: March 1, 2024
Expiration Date: November 1, 2026
Expert: David Mischoulon, M.D.
Medical Editor: Paz Badía, M.D.
Relevant Financial Disclosures:
David Mischoulon declares the following interests:
- Nordic Naturals: Received research support (medication and placebo for a study)
- heckel medizintechnik GmbH: Received research support (Whole Body Hyperthermia device for research study)
- MGH Clinical Trials Network and Institute (CTNI): Received salary support
All of the relevant financial relationships listed above have been mitigated by Medical Academy and the Psychopharmacology Institute.
None of the others faculty, planners, and reviewers for this educational activity have relevant financial relationships to disclose during the last 24 months with ineligible companies whose primary business is producing, marketing, selling, re-selling, or distributing healthcare products used by or on patients.
Contact Information: For questions regarding the content or access to this activity, contact us at support@psychopharmacologyinstitute.com
Instructions for Participation and Credit:
Participants must complete the activity online during the valid credit period that is noted above.
Follow these steps to earn CME credit:
-
View the required educational content provided on this course page.
-
Complete the Post Activity Evaluation for providing the necessary feedback for continuing accreditation purposes and for the development of future activities. NOTE: Completing the Post Activity Evaluation after the quiz is required to receive the earned credit.
-
Download your certificate.
Accreditation Statement
This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the accreditation requirements and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education through the joint providership of Medical Academy LLC and the Psychopharmacology Institute. Medical Academy is accredited by the ACCME to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Credit Designation Statement
Medical Academy designates this enduring activity for a maximum of 0.75 AMA PRA Category 1 credit(s)™. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.