Slides and Transcript
Slide 1 of 13
Now that you understand a little bit about the role of tyramine and how it works, the question is: What do you tell patients?
Slide 2 of 13
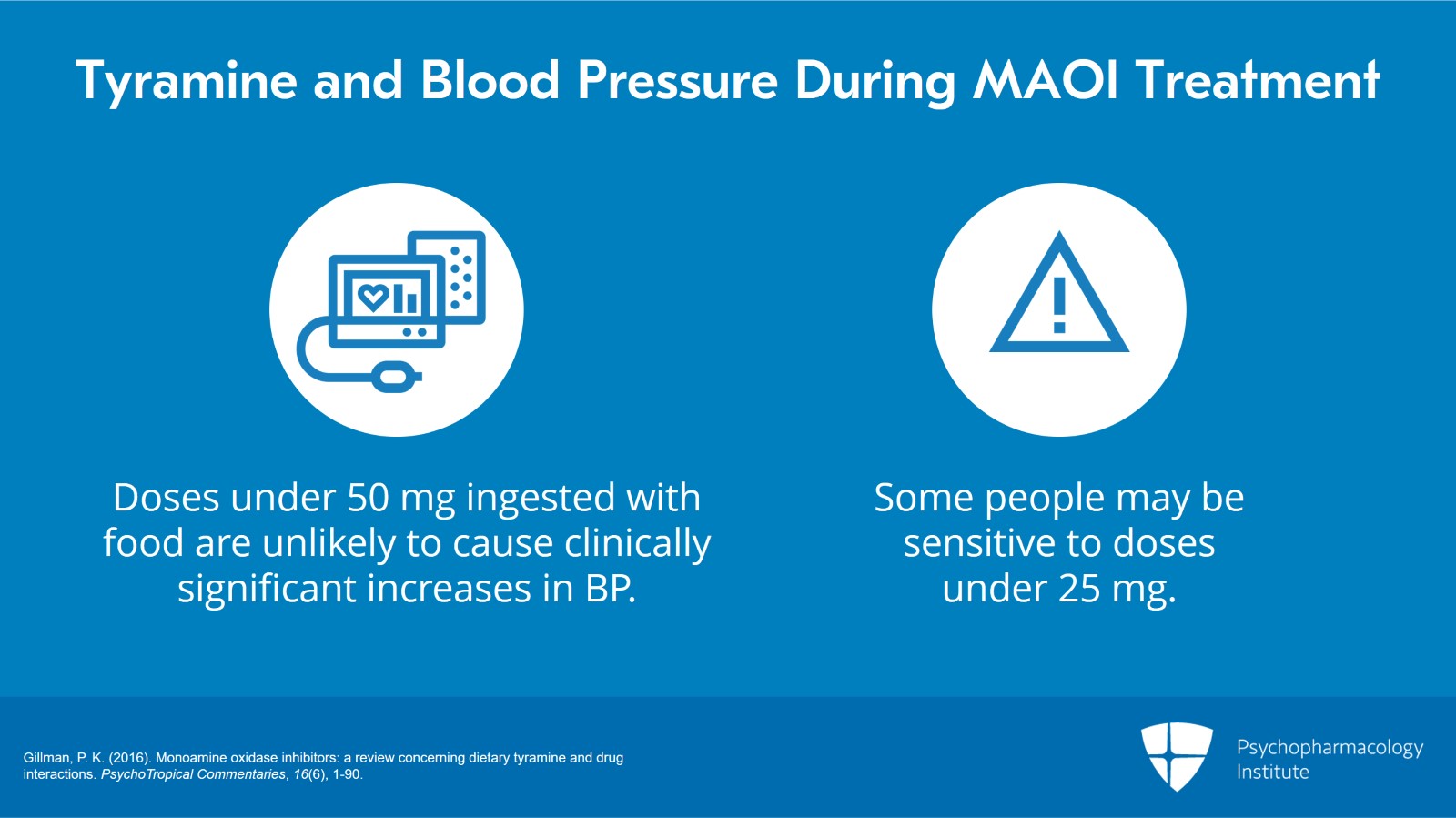
Although administering pure tyramine capsules in doses as low as 10 mg can induce a measurable change in systolic blood pressure, when ingested as part of food, tyramine doses under 50 mg are unlikely to cause an increase in blood pressure sufficient to warrant clinical intervention although some individuals might be sensitive to doses under 25 mg.
*References*
References:
- Gillman, P. K. (2016). Monoamine oxidase inhibitors: a review concerning dietary tyramine and drug interactions. PsychoTropical Commentaries, 16(6), 1-90.
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.
Slide 3 of 13
When discussing with patients safety issues related to diet, here are a few important concepts to remember. In an era when the tyramine content of foods was much higher, the early ‘60s, and often unregulated and MAOI users received no dietary guidance, only 14 deaths were reported among an estimated 1.5 million patients who took MAOIs.
*References*
References:
- Meyer, J. M. (2017). A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors: A better understanding of the risks can lead to increased use of these highly effective agents. Current Psychiatry, 16(12), 15-23.
Slide 4 of 13
As mentioned previously, MAOIs do not raise blood pressure and their use is associated with orthostasis in some patients.
Routine exercise or other vigorous activities such as weightlifting can raise systolic pressure well above 200 mmHg. Moreover, routine baseline systolic pressures ranging from 180 to 220 mmHg do not increase the risk of subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Hospital evaluation is needed only if a substantial amount of tyramine is ingested, estimated greater than 100 mg, and self-monitoring shows a systolic blood pressure greater than 220 over a prolonged period, for example, two hours.
*References*
References:
- Meyer, J. M. (2017). A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors: A better understanding of the risks can lead to increased use of these highly effective agents. Current Psychiatry, 16(12), 15-23.
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.
Slide 5 of 13
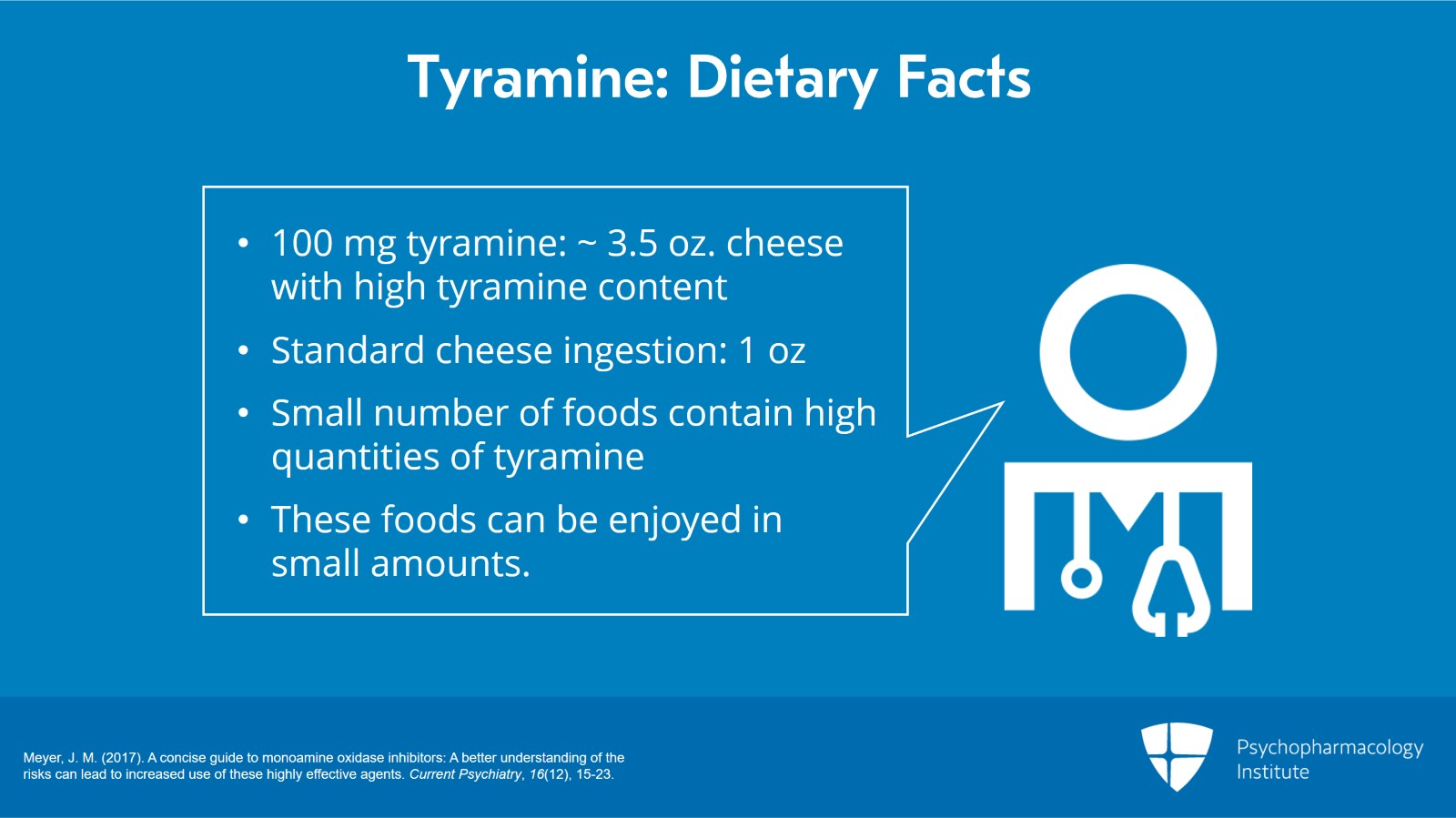
Ingestion of 100 mg of tyramine would almost certainly have to be intentional as it would require one to consume 3 1/2 ounces of the most highly tyramine-laden cheeses.
For most people, a standard amount of cheese ingestion is maybe 1 ounce.
So one is to emphasize to patients that only a small number of highly aged cheeses, foods and sauces contain high quantities of tyramine and that even these foods can still be enjoyed in small amounts.
*References*
References:
- Meyer, J. M. (2017). A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors: A better understanding of the risks can lead to increased use of these highly effective agents. Current Psychiatry, 16(12), 15-23.
Slide 6 of 13
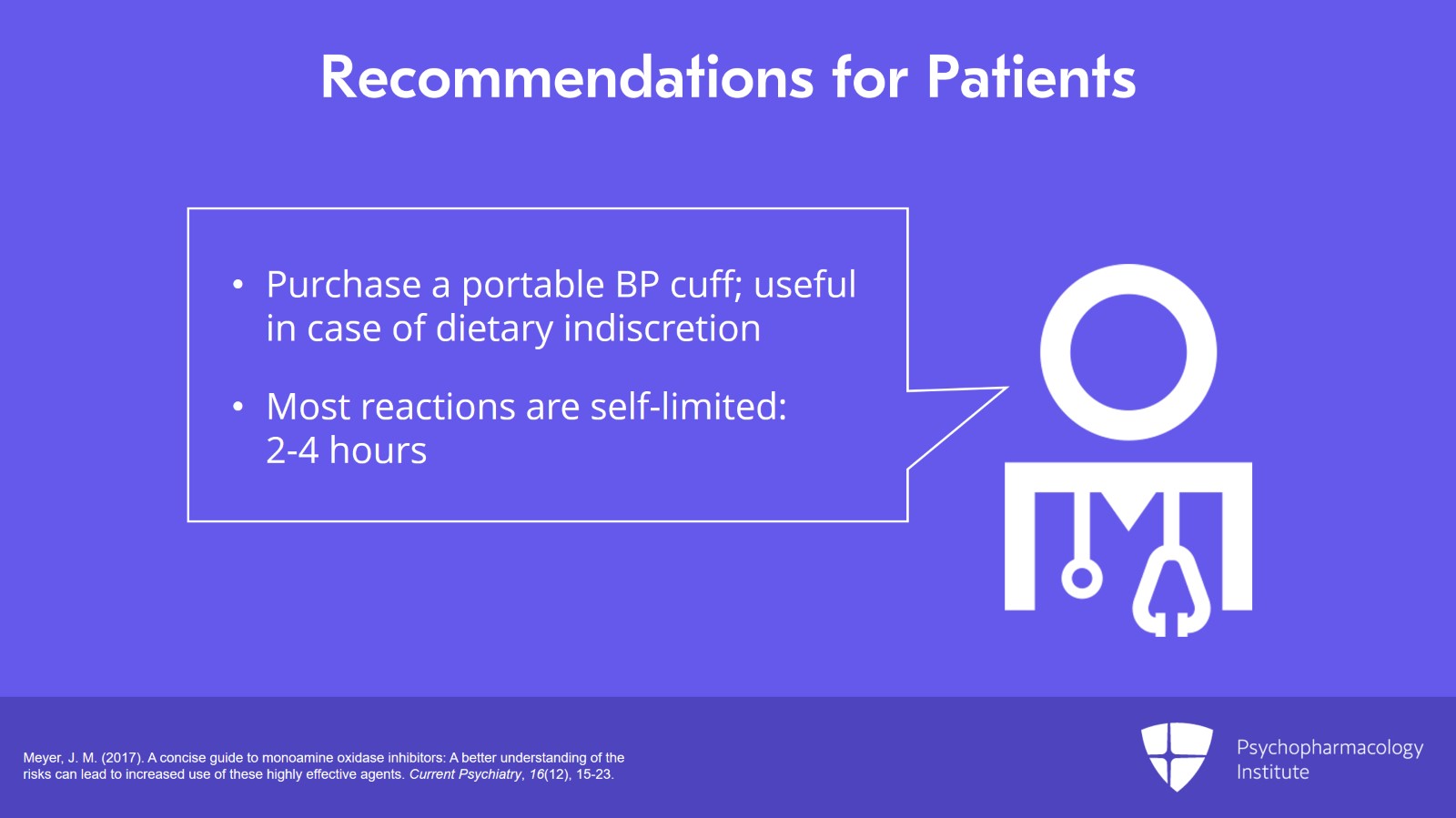
All patients who are prescribed an MAOI should also purchase a portable blood pressure cuff for those rare instances when a dietary indiscretion may have occurred and the person experiences a headache within one to two hours after the ingestion. Most reactions are self-limited and resolve over two to four hours.
*References*
References:
- Meyer, J. M. (2017). A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors: A better understanding of the risks can lead to increased use of these highly effective agents. Current Psychiatry, 16(12), 15-23.
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.
Slide 7 of 13
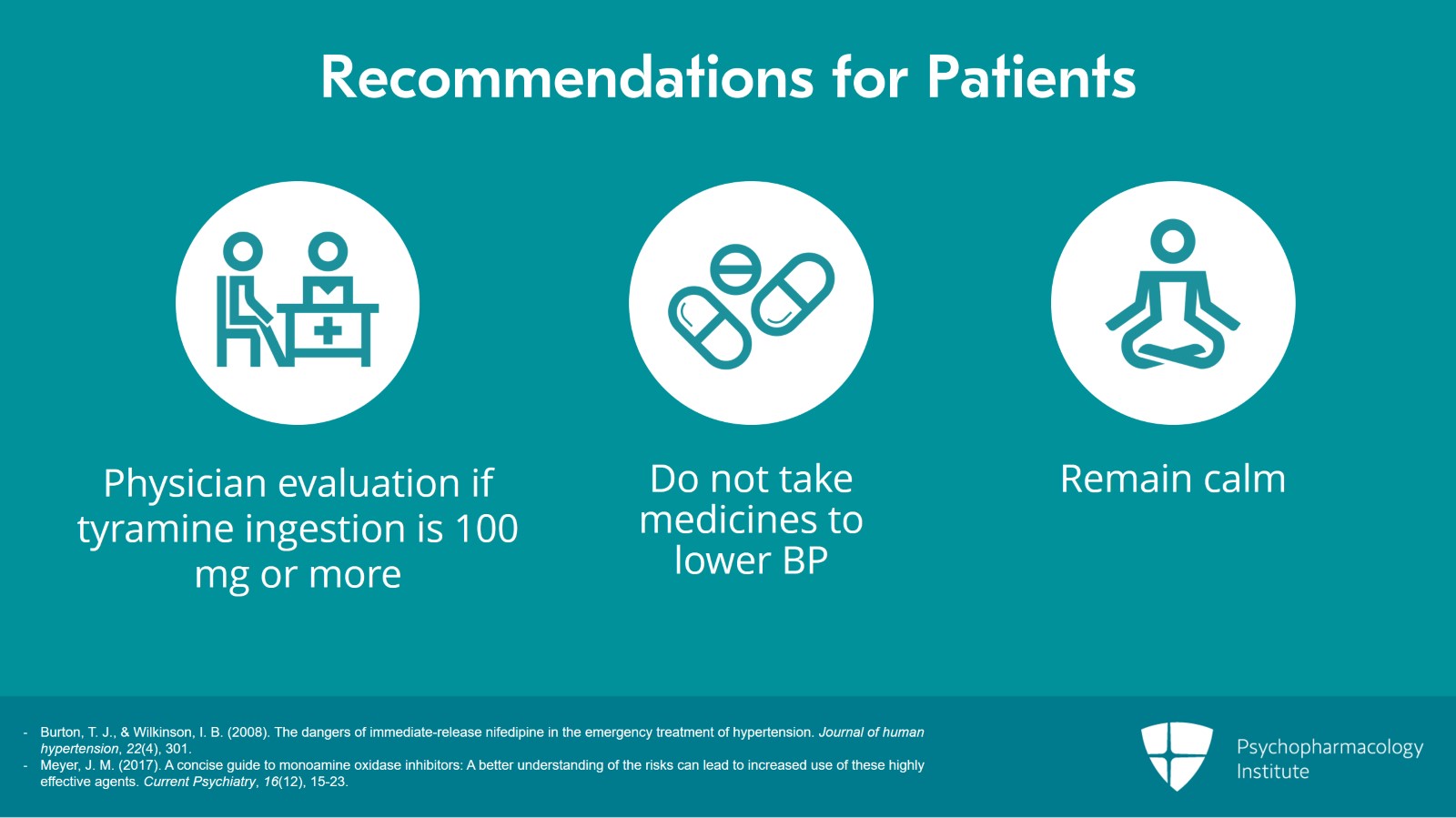
Patients who ingest 100 mg tyramine or more should be evaluated by a physician. Under no circumstances should a patient ever be given a prescription for nifedipine or other medicines that can abruptly lower blood pressure because this may result in complications including myocardial infarction. Instead, patients should be counseled to remain calm.
*References*
References:
- Burton, T. J., & Wilkinson, I. B. (2008). The dangers of immediate-release nifedipine in the emergency treatment of hypertension. Journal of human hypertension, 22(4), 301.
- Meyer, J. M. (2017). A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors: A better understanding of the risks can lead to increased use of these highly effective agents. Current Psychiatry, 16(12), 15-23.
Slide 8 of 13
Some clinicians endorse the use of low doses of benzodiazepines, for example the equivalent of alprazolam 0.5 mg, to facilitate patient’s relaxing because anxiety elevates blood pressure.
A recent emergency room study of patients with an initial systolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 160 or diastolic pressure greater than or equal to 100 without end-organ damage demonstrated that alprazolam 0.5 mg was as effective as an ACE inhibitor in lowering blood pressure.
Of course, the prescription for alprazolam has to be limited to those who do not have a history of substance abuse. The point being is that anxiety more so than tyramine ingestion is often the reason the blood pressure is elevated.
Getting patients to relax possibly with the use of a low-dose benzodiazepine can often avert an unnecessary trip to the emergency room.
*References*
References:
- Yilmaz, S., Pekdemir, M., Tural, Ü., & Uygun, M. (2011). Comparison of alprazolam versus captopril in high blood pressure: a randomized controlled trial. Blood pressure, 20(4), 239-243.
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.
Slide 9 of 13
Also, tell patients that if a food is unfamiliar and highly aged or fermented they should avoid it until they can further inquire about the tyramine content.
*References*
References:
- Meyer, J. M. (2017). A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors: A better understanding of the risks can lead to increased use of these highly effective agents. Current Psychiatry, 16(12), 15-23.
Slide 10 of 13
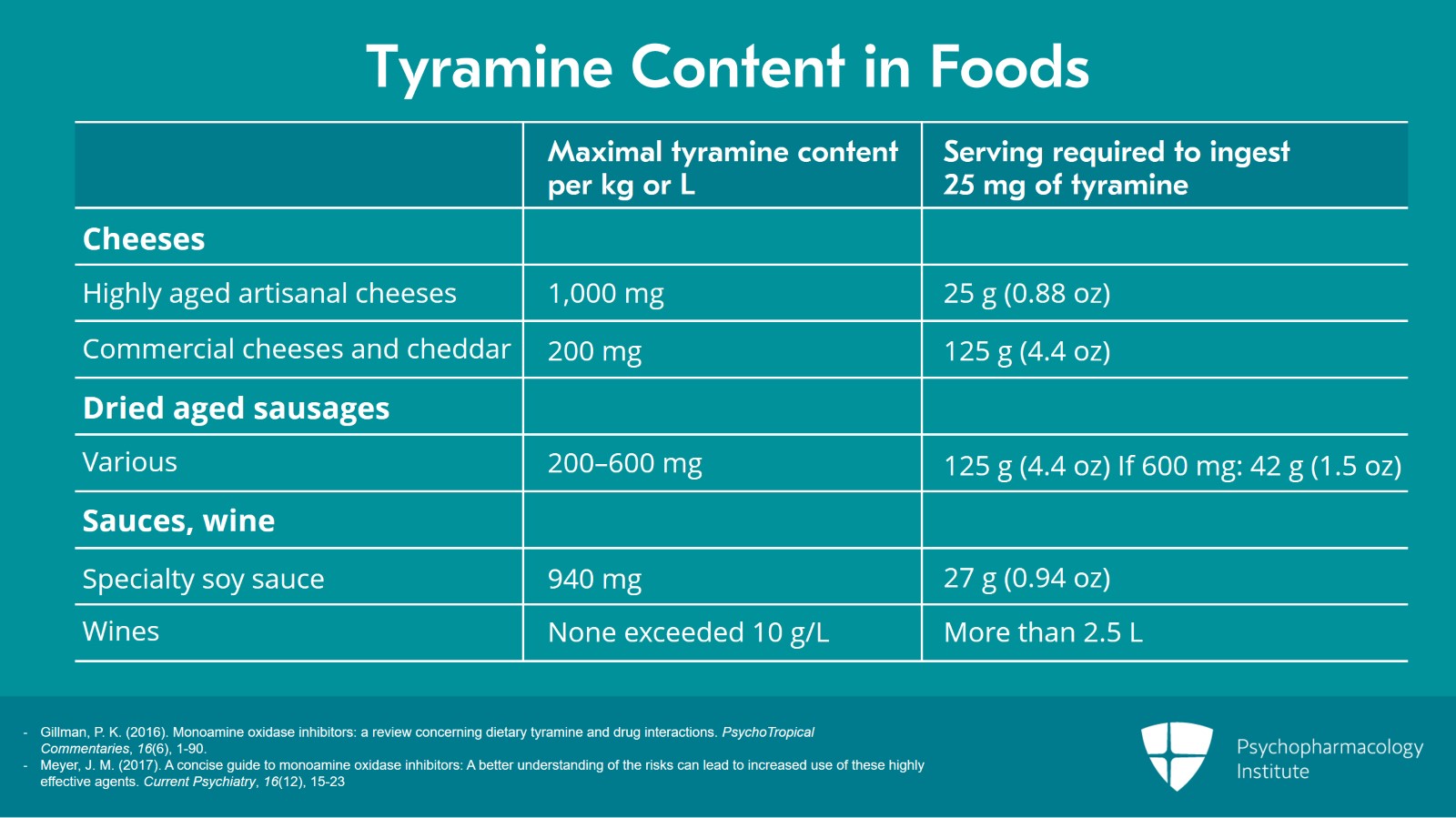
In his extensive review, Professor Gillman provides the tyramine content of an exhaustive list of cheeses, aged meats and sauces, some of which are abstracted in the table attached to this lecture.
For other products, patients can often obtain information directly from the manufacturer. In many parts of the world, assays for tyramine content are required as a demonstration of adequate product safety procedures. And even the most highly aged cheeses with a tyramine content of 1000 mg/kg can still be enjoyed in small amounts. Most products will require heroic intake to achieve clinically significant tyramine ingestion, meaning the equivalent of tyramine doses greater than 25 mg.
*References*
References:
- Gillman, P. K. (2016). Monoamine oxidase inhibitors: a review concerning dietary tyramine and drug interactions. PsychoTropical Commentaries, 16(6), 1-90.
- Meyer, J. M. (2017). A concise guide to monoamine oxidase inhibitors: A better understanding of the risks can lead to increased use of these highly effective agents. Current Psychiatry, 16(12), 15-23
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.
Slide 11 of 13
The key points here are that very few people will ingest more than 25 mg of tyramine even when consuming high tyramine content foods.
For patients on MAOIs, ingestion of amounts under 50 mg is unlikely to cause clinically significant blood pressure effects.
Even in the early 1960s when food tyramine content was much higher and MAOI users received no dietary guidance, only 14 deaths were reported among an estimated 1.5 million patients who took MAOIs.
Slide 12 of 13
Hospital evaluation is needed only if a substantial amount of tyramine is ingested, this is estimated to be 100 mg or more, and self-monitoring shows a systolic pressure greater than or equal to 220 mmHg over a prolonged period, for example, two hours. Ingestion of 100 mg of tyramine would almost have to be intentional as it will require one to consume 3 1/2 ounces of the most highly tyramine-laden cheeses.
Patients should never be given prescriptions for blood pressure lowering medicines as their use may cause significant hypotension and related complications including myocardial infarction.
They should, however, purchase a portable blood pressure cuff and be counseled that anxiety is often a big a contributor to blood pressure elevation.
Free Files
Download PDF and other files
Success!
Check your inbox, we sent you all the materials there.